React (React.js or ReactJS)
Tools
Rule
All React components must act like pure functions with respect to their props.
components distribution
https://github.com/callemall/material-ui
https://github.com/krasimir/react-place
http://krasimirtsonev.com/blog/article/distributing-react-components-babel-browserify-webpack-uglifyjs
https://github.com/airbnb/javascript/tree/master/react
使用react做的网站
- https://www.refactor.io/
- https://www.airbnb.com/s
- https://www.pinterest.com/
- https://marvelapp.com/9e8g1gj/screen/31751929
Define React component, the ES5,ES6,ES6+ way
Define component: ES5 vs ES6+
// The ES5 way
var Photo = React.createClass({
handleDoubleTap: function(e) { … },
render: function() { … },
});
// The ES6+ way
class Photo extends React.Component {
handleDoubleTap(e) { … }
render() { … }
}
Define componentWillMount: ES5 vs ES6+
// The ES5 way
var EmbedModal = React.createClass({
componentWillMount: function() { … },
});
// The ES6+ way
class EmbedModal extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
// Operations usually carried out in componentWillMount go here
…
}
}
Define prop types, initilal state and prop defaults: ES5 vs ES6+
// The ES5 way
var Video = React.createClass({
getDefaultProps: function() {
return {
autoPlay: false,
maxLoops: 10,
};
},
getInitialState: function() {
return {
loopsRemaining: this.props.maxLoops,
};
},
propTypes: {
autoPlay: React.PropTypes.bool.isRequired,
maxLoops: React.PropTypes.number.isRequired,
posterFrameSrc: React.PropTypes.string.isRequired,
videoSrc: React.PropTypes.string.isRequired,
},
});
// The ES6+ way
class Video extends React.Component {
static defaultProps = {
autoPlay: false,
maxLoops: 10,
}
static propTypes = {
autoPlay: React.PropTypes.bool.isRequired,
maxLoops: React.PropTypes.number.isRequired,
posterFrameSrc: React.PropTypes.string.isRequired,
videoSrc: React.PropTypes.string.isRequired,
}
state = {
loopsRemaining: this.props.maxLoops,
}
}
Binding this for component’s instance methods: ES5 vs ES6+
// The ES5 way
// Autobinding, brought to you by React.createClass
var PostInfo = React.createClass({
handleOptionsButtonClick: function(e) {
// Here, 'this' refers to the component instance.
this.setState({showOptionsModal: true});
},
});
// The ES6+ way
// Manually bind, wherever you need to
class PostInfo extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
// Manually bind this method to the component instance...
this.handleOptionsButtonClick = this.handleOptionsButtonClick.bind(this);
}
handleOptionsButtonClick(e) {
// ...to ensure that 'this' refers to the component instance here.
this.setState({showOptionsModal: true});
}
}
// Another ES6+ way
// Using Arrow functions and property initializers
class PostInfo extends React.Component {
handleOptionsButtonClick = (e) => {
// The body of ES6 arrow functions share the same lexical this as the code that surrounds them
this.setState({showOptionsModal: true});
}
handleOptionsButtonClick2(e) {
console.log(this); // undefined
}
}
Another ES6+ way
- Using bind operator
::(syntactic sugar) (more about bind operator) - Use
Function.prototype.bind()method
class PostInfo extends React.Component {
handleChange(e) {
console.log(this); // PostInfo
this.setState({value: event.target.value});
}
handleBlur(e) {
console.log(this); // PostInfo
this.setState({value: event.target.value});
}
render() {
return (
<input
onChange={::this.handleChange}
onBlur={this.handleBlur.bind(this)} >
)
}
}
Counter examples: ES6+ vs ES6 vs ES5
The ES6+ way
ES7+ Property Initializers, inspired by TypeScript’s property initializers.
See more https://facebook.github.io/react/blog/2015/01/27/react-v0.13.0-beta-1.html#es7-property-initializers, https://babeljs.io/blog/2015/06/07/react-on-es6-plus#property-initializers.
Use babel presets [preset-stage-2.transform-class-properties] to transform.
export class Counter extends React.Component {
static contextTypes = {
router: React.PropTypes.object.isRequired
}
static propTypes = { initialCount: React.PropTypes.number };
static defaultProps = { initialCount: 0 };
state = { count: this.props.initialCount };
tick() {
this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });
}
render() {
return (
<div onClick={this.tick.bind(this)}>
Clicks: {this.state.count}
</div>
);
}
}
The ES6 way
// https://facebook.github.io/react/docs/reusable-components.html#es6-classes
export class Counter extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {count: props.initialCount};
this.tick = this.tick.bind(this);
}
tick() {
this.setState({count: this.state.count + 1});
}
render() {
return (
<div onClick={this.tick}>
Clicks: {this.state.count}
</div>
);
}
}
Counter.propTypes = { initialCount: React.PropTypes.number };
Counter.defaultProps = { initialCount: 0 };
The ES5 way
// https://facebook.github.io/react/tips/props-in-getInitialState-as-anti-pattern.html
var Counter = React.createClass({
propTypes: {
initialCount: React.PropTypes.number
},
getDefaultProps() {
return {
initialCount: 0
};
},
getInitialState: function() {
// naming it initialX clearly indicates that the only purpose
// of the passed down prop is to initialize something internally
return {count: this.props.initialCount};
},
handleClick: function() {
this.setState({count: this.state.count + 1});
},
render: function() {
return <div onClick={this.handleClick}>{this.state.count}</div>;
}
});
References
boilerplate
with hot reload
Lifecycle of a component
React style
两种方式,一种使用内联的style,因为这样可以和React无缝集合,而且不用考虑外部的CSS了,所以好多React组件在使用这个方法。
<Com style={ {width: '50px', height: '100px'} } />
另外一个就是使用className来指定一个selector了,就像传统的方法一样。
<Com className='table' />
Hot reload
- react-hot-loader
- react-transform-hmr
- babel-preset-react-hmre
Integrating React.js into Existing (jQuery) Web Applications
index.html
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Sample App</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id='root'>
</div>
<script>
var foo = {
bar: "test",
cb: function (p) {
alert(p);
}
};
</script>
<script src="/static/bundle.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
index.js
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import App from './App';
ReactDOM.render(<App foo={foo} />, document.getElementById('root'));
App.js
import React, { Component, PropTypes } from 'react';
export default class App extends Component {
static PropTypes = {
foo: PropTypes.object.isRequired
}
onButtonClick() {
const foo = this.props.foo;
foo.cb("aaa");
}
render() {
const foo = this.props.foo;
return (
<div>
<h1>Hello, world.{foo.bar}</h1>
<button onClick={::this.onButtonClick}>Submit</button>
</div>
);
}
}
React Developer Tools
https://github.com/facebook/react-devtools
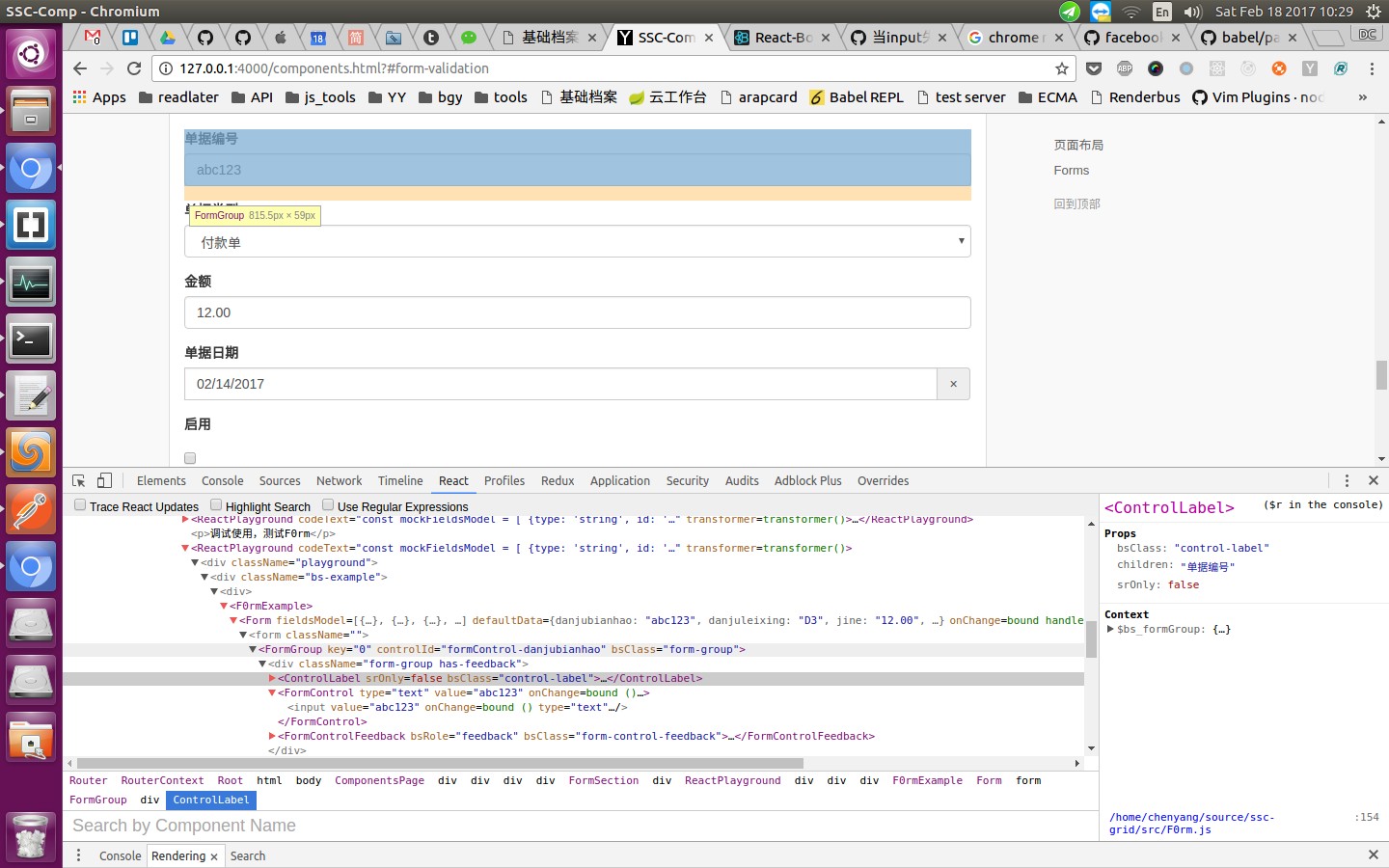
Show the source file & line number of react elements
The babel-plugin-transform-react-jsx-source will adds source file and line number to JSX elements.
Show the source file & line number of created react elements, at the bottom of the right panel.
Webpack config
https://github.com/facebookincubator/create-react-app/tree/master/packages/react-scripts/config
react no jsx example
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<!-- Latest compiled and minified CSS -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/latest/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<!-- Optional theme -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/latest/css/bootstrap-theme.min.css">
<script src="https://npmcdn.com/react@15.5.4/dist/react-with-addons.js"></script>
<script src="https://npmcdn.com/react-dom@15.5.4/dist/react-dom.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-bootstrap@0.31.0/dist/react-bootstrap.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="container">
<!-- This element's contents will be replaced with your component. -->
</div>
<script>
var rootElement =
React.createElement('div', {},
React.createElement('h1', {}, "Contacts"),
React.createElement('Button', {}, "Contacts"),
React.createElement('ul', {},
React.createElement('li', {},
React.createElement('h2', {}, "James Nelson"),
React.createElement('a', {href: 'mailto:james@jamesknelson.com'}, 'james@jamesknelson.com')
),
React.createElement('li', {},
React.createElement('h2', {}, "Joe Citizen"),
React.createElement('a', {href: 'mailto:joe@example.com'}, 'joe@example.com')
)
)
)
ReactDOM.render(rootElement, document.getElementById('container'))
</script>
</body>
</html>
Comments
comment out jsx
<div>
<span>test1</span>
{/*<span>test2</span>*/}
</div>
comment out props
<input
id="name"
// placeholder="test
/>
If you want to test out how some specific JSX is converted into JavaScript, you can try out Babel REPL
Event
onClickto register an event handler for the bubbling phaseonClickCaptureto register an event handler for the capture phase
Application structure
- API service - https://medium.com/@alexmngn/how-to-better-organize-your-react-applications-2fd3ea1920f1
npm packages compare
styles
- react-with-styles 跟bootstrap样式不好集成
patterns
containers vs components
- https://medium.com/@dan_abramov/smart-and-dumb-components-7ca2f9a7c7d0
- https://medium.com/@learnreact/container-components-c0e67432e005
HTML form element
<form method="POST" action="http://10.3.14.238/fireport/rptfilemanage/download">
<input type="hidden" name="modid" value={rowObj.id} />
<input type="hidden" name="modcode" value={rowObj.code} />
<input type="submit" value="Export" />
</form>
You may also like to know HTML attributes supported by React
i18n
A demo: https://github.com/react-boilerplate/react-boilerplate